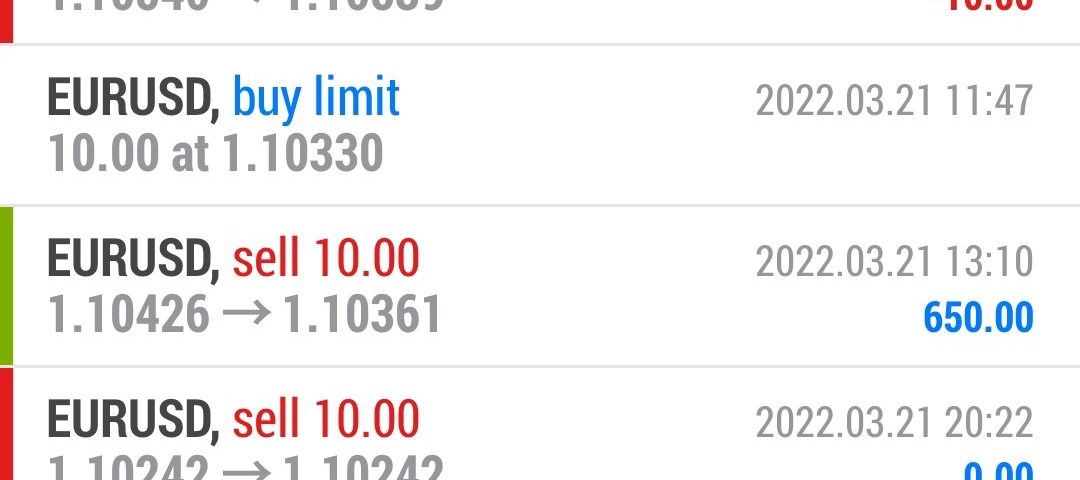
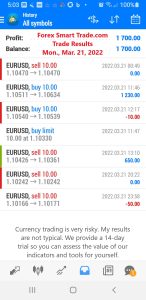
Forex Trade Results March 21, 2022
Forex Trade Results March 18, 2022
March 21, 2022
Forex Trade Results March 22, 2022
March 22, 2022What is Forex Trading?
Forex trading is similar to the currency exchange you may do while traveling abroad. A trader buys one currency and sells another. The exchange rate constantly fluctuates based on supply and demand.
Currencies are traded in the foreign exchange market. It is a global marketplace that’s open 24 hours a day Monday through Friday. All forex trading is conducted over the counter (OTC), meaning there’s no physical exchange (as there is for stocks) and a global network of banks and other financial institutions oversee the market (instead of a central exchange, like the New York Stock Exchange).
A vast majority of trade activity in the forex market occurs between institutional traders. Institutional traders are people who work for banks, fund managers, and multinational corporations. These traders don’t necessarily intend to take physical possession of the currencies themselves. They may simply be speculating about or hedging against future exchange rate fluctuations.
A forex trader might buy U.S. dollars (and sell euros), for example, if she believes the dollar will strengthen in value. And then be able to buy more euros in the future. Meanwhile, an American company with European operations could use the forex market as a hedge. A hedge would be when the euro weakens, meaning the value of their income earned there falls.
What is Forex Trading?
Learn How To Successfully Trade Forex
If you’d like to earn extra income trading on the Forex market, consider learning how to currency trade with Forex Smart Trade. With their super-accurate proprietary trading tools and best-in-the-business, personalized one-on-one training, you’ll be successful. Check out the Forex Smart Trade webinar. It shows one of their trader’s trading and how easy, intuitive, and accurate the tools are. Or try the Forex Smart Trade 14-day introductory trial for just TEN dollars.